Solutions
| Developing a
good solution requires an understanding of the
organization and the functionality end users need to
support them. There may be multiple departments within the
same organization that share the system(s), but have
different roles, needs and implementations. At WillowFalls Consulting, we are trained in Incident Command System, Business Continuity Planning, Security and Emergency Management, to help us understand clients requirements and what they are trying to accomplish with their communications and security systems. |
|
Increasing efforts for information sharing,
risk mitigation and cost reduction, are pushing organizations
towards greater sharing and coordination of resources. The
organizational lines between Security, Emergency Management,
Business Continuity and Public Safety, overlap in many ways,
making it impossible to address one area, without considering
the others.
WillowFalls Consulting provides a holistic view to solutions for communications and security. Communications is no longer about each group or agency having dedicated frequencies and equipment. Interoperability and information sharing, lack of frequencies and cost reduction are driving agencies and organizations towards the need for shared infrastructure.
Support is a key element of operations, and with communications and security systems now IP network connected, IT support is as important as RF technicians. Understanding the support requirements, costs and who is responsible for each support component, before selecting a new system, ensures that ongoing operational funding and staffing is put in place as part of implementation.
WillowFalls Consulting provides a holistic view to solutions for communications and security. Communications is no longer about each group or agency having dedicated frequencies and equipment. Interoperability and information sharing, lack of frequencies and cost reduction are driving agencies and organizations towards the need for shared infrastructure.
Support is a key element of operations, and with communications and security systems now IP network connected, IT support is as important as RF technicians. Understanding the support requirements, costs and who is responsible for each support component, before selecting a new system, ensures that ongoing operational funding and staffing is put in place as part of implementation.
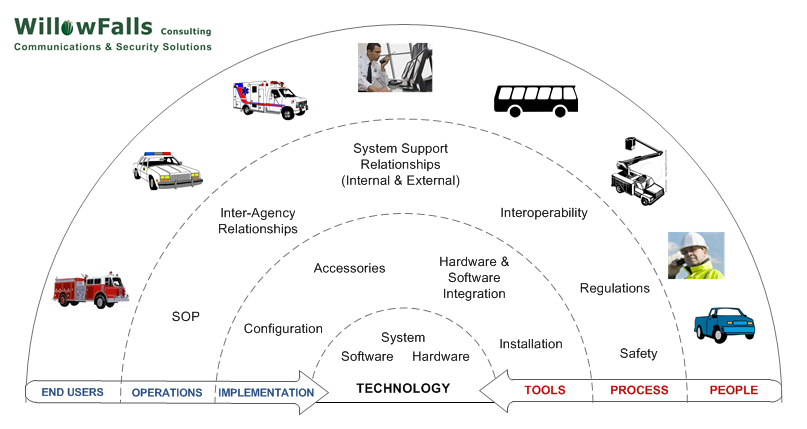
Effectiveness Is More Than Technology Selection
Implementing an effective solution involves more than technology
selection. There are several other important activities that need
to take place in order to make sure that the technology gets
implemented correctly, so it supports the organization.Getting The Requirements Right
Getting the requirements right means understanding the root problems end users and the organization need solved. The requirements written into an RFP need to ensure that these root problems are addressed. The small details often impact end users the most.Understanding Ongoing Costs
The organization needs to understand the ongoing effort and support costs for the requirements they want to include. Capital funding will cover the equipment purchase, but there will be ongoing costs that need to be supported from yearly operations budgets. Costs may include additional staff effort to manage capabilities such as encryption, the cost for outside services such as maintenance contracts and the cost for consumable items such as batteries.Governance & SOPs
Everything needs some Governance, to define the responsibilities and rules for management and use. This can be as simple as a single paragraph, or as complicated as a multi-partner agreement. To be effective, governance must be based on a full understanding of the impacts and responsibilities of implementing, operating and maintaining the capability or system.Training, Exercises & Daily Usage
"Practice, Practice, Practice" and "Use It Or Lose It", are two phases that apply to any capability. Often systems are implemented with capabilities that are not documented and not practiced, so as people change jobs, the knowledge and understanding is lost. In a crisis people don't have time to think, so using the systems capabilities should be second nature.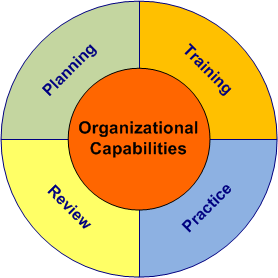 |
In order for technology implementations to
be effective, there must be ongoing updates to training
and exercise plans, as well as daily use. Planning and review take lessons learned from training and practice, to make improvements to training and SOPs, as part of a continuous improvement process. In a crisis, the organizational capabilities available will be a result of the ongoing training, practice, review and improvement process. |